Identifying open ports on a target system is extremely
important step to defining the attack surface of a target system. Open
ports correspond to the networked services that are running on a system.
Programming errors or implementation flaws can make these services susceptible to security and it also may cause compromise entire system. to work out the possible attack vectors, we must first enumerate the open ports on all of the remote systems.
These open ports correspond to services which will be addressed with either UDP or TCP traffic. Both TCP and UDP are transport protocols. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is that the more widely used of the 2 and provides connection-oriented communication. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) may be a non connection-oriented protocol that’s sometimes used with services that speed of transmission is more important than data integrity.
The penetration testing method used to determine these services is called port scanning. In our this article we are going to cover some basic theory about the port scanning then we can easily understand the work methodology of any port scanner tools.
UDP Port Scanning
Because TCP may be a more widely used transport layer protocol, services that operate over UDP are frequently forgotten. Despite the natural tendency to overlook UDP services, it’s absolutely critical that these services are enumerated to accumulate an entire understanding of the attack surface of any given target. UDP scanning can often be challenging, tedious, and time consuming. It’s important to know the 2 different approaches to UDP scanning which will be used.
In the first method, is to rely exclusively on ICMP port-unreachable responses. this sort of scanning relies on the idea that any UDP ports that aren’t related to a live service will return an ICMP port-unreachable response, and a scarcity of response is interpreted as a sign of a live service. While this approach are often effective in some circumstances, it also can return inaccurate leads to cases where the host isn’t generating port-unreachable responses, or the port-unreachable replies are rate limited or they’re filtered by a firewall.
In the second method, which is addressed within the second and third recipes, is to use service-specific probes to aim to solicit a response, which might indicate that the expected service is running on the targeted port. While this approach are often highly effective, it also can be very time consuming.
TCP Port Scanning
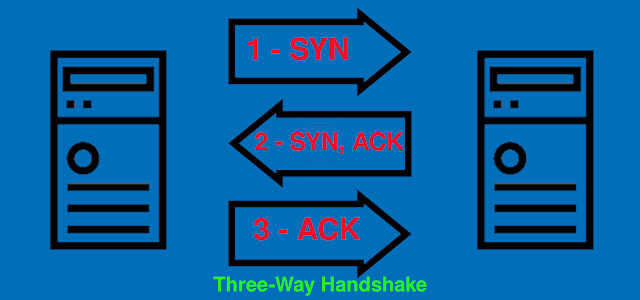
In this article, many different methods to TCP scanning will be covered. These methods include stealth scanning, connect scanning, and zombie scanning. To understand how these scanning techniques work, it is important to understand how TCP connections are established and worded. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, and data is only transported over TCP after a connection has been established between two systems. The process associated with establishing a TCP connection is often referred to as the three-way handshake. This name alludes to the three steps involved in the connection process. The following diagram shows this process in a graphical form:
From the above picture we can see that a TCP SYN packet is sent from the device that wishes to establish a connection with a port of the device that it desires to connect with. If the service associated with the receiving port grants the connection, it will reply to the requesting system with a TCP packet that has both the SYN and ACK bits activated. The connection is established that time when the requesting system responds with a TCP ACK response. This three-step process (three-way handshake) establishes a TCP session between the two systems. All of the TCP port scanning techniques will perform some varieties of this process to identify live services on remote hosts.
Connect scanning and stealth scanning both are quite easy to know . Connect scanning wont to establish a full TCP connection for each port that’s scanned. that’s to mention , for each port that’s scanned, the complete three-way handshake is completed. If a connection is successfully established, the port is then seems to be open.
In the case of stealth scanning doesn’t establish a full connection. Stealth scanning is additionally referred as SYN scanning or half-open scanning. for every port that’s scanned, one SYN packet is shipped to the destination port, and every one ports that reply with a SYN+ACK packet are assumed to be running live services. Since no final ACK is shipped from the initiating system, the connection is left half-open. this is often mentioned as stealth scanning because logging solutions that only record established connections won’t record any evidence of the scan. the ultimate method of TCP scanning which will be discussed during this chapter may be a technique called zombie scanning. the aim of zombie scanning is to map open ports on a foreign system without producing any evidence that you simply have interacted thereupon system. The principles behind how zombie scanning works are somewhat complex. perform the method of zombie scanning with the subsequent steps:
- Identify a remote system for our zombie host. The system should have the some characteristics, they are following:
- The system need to be idle and does not communicate actively with other systems over the network.
- The system need to use an incremental IPID sequence.
- Send a SYN+ACK packet to this zombie host and record the initial IPID value.
- Send a SYN packet with a spoofed source IP address of the zombie system to the scan target system.
- Depending on the status of the port on the scan target, one of the following two things will happen:
- If the port is open, the scan target will return a SYN+ACK packet to the zombie host, which it believes sent the original SYN request. In this case, the zombie host will respond to this unsolicited SYN+ACK packet with an RST packet and thereby increment its IPID value by one.
- If the port is closed, the scan target will return an RST response to the zombie host, which it believes sent the original SYN request. This RST packet will solicit no response from the zombie, and the IPID will not be incremented.
- Send another SYN+ACK packet to the zombie host, and evaluate the final IPID value of the returned RST response. If this value has incremented by one, then the port on the scan target is closed, and if the value has incremented by two, then the port on the scan target is open.
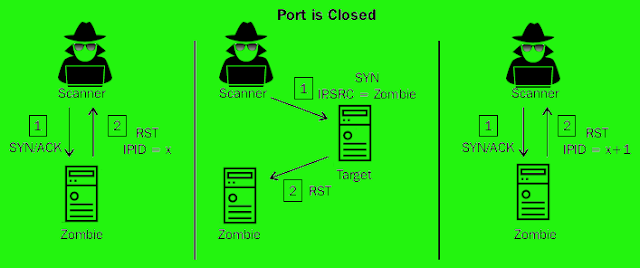
The following image shows the interactions that take place when we use a zombie host to scan an open port:
To perform a zombie scan, an initial SYN+ACK request should be sent to the zombie system to work out the present IPID value within the returned RST packet. Then, a spoofed SYN packet is shipped to the scan target with a source IP address of the zombie system. If the port is open, the scan target will send a SYN+ACK response back to the zombie. Since the zombie didn’t actually send the initial SYN request, it’ll interpret the SYN+ACK response as unsolicited and send an RST packet back to the target, thereby incrementing its IPID by one.
Finally, another SYN+ACK packet should be sent to the zombie, which can return an RST packet and increment the IPID another time. An IPID that has incremented by two from the initial response is indicative of the very fact that each one of those events have transpired which the destination port on the scanned system is open. Alternatively, if the port on the scan target is closed, a special series of events will transpire, which can only cause the ultimate RST response IPID value to increment by one.
The following picture is an demo of the sequence of events comes with the zombie scan of a closed port:
If the destination port on the scan target is closed, an RST packet are going to be sent to the zombie system in response to the initially spoofed SYN packet. Since the RST packet solicits no response, the IPID value of the zombie system won’t be incremented. As a result, the ultimate RST packet returned to the scanning system in response to the SYN+ACK packet will have the IPID incremented by just one .
This process are often performed for every port that’s to be scanned, and it are often wont to map open ports on a remote system without leaving any evidence that a scan was performed by the scanning system.
This is how port scanning methods works. In this article we tried to do something different, this is not about any tool but if we are using Kali Linux or we are in cybersecurity field then we should have some technical knowledge. Hope this article also get love. This is all for today.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.