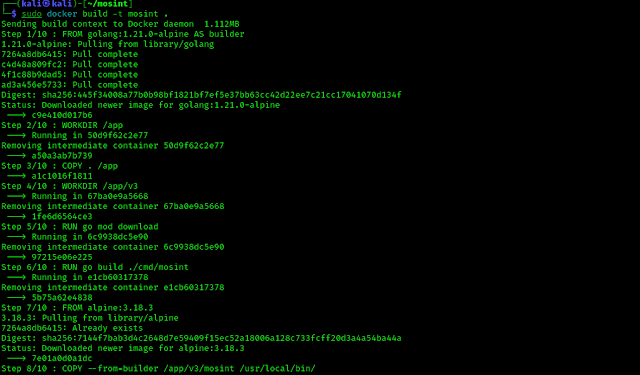
Information gathering is a very crucial part of cybersecurity. If our target is a web server then we need to know a lot of things about it. We use various tools to do this jobs easily.
SSLyze is a fast and powerful python tool that can be used to analyze the SSL configuration of a server by connecting to it. SSLyze comes pre-installed with Kali Linux.
It allows us to analyze the SSL/TLS configuration of a server by connecting to it, in order to detect various issues (bad certificate, weak cipher suites, Heartbleed, ROBOT, TLS 1.3 support, etc).
SSLyze can either be used as command line tool or as a Python library.
Key-Features of SSLyze
- Multi-processed and multi-threaded scanning (it’s really fast).
- SSL 2.0/3.0 and TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 compatibility.
- Fully documented Python API, in order to run scans and process the results directly from Python.
- Support for TLS 1.3 and early data (0-RTT) testing.
- Scans are automatically dispatched among multiple workers, making them very fast.
- Performance testing: session resumption and TLS tickets support.
- Security testing: weak cipher suites, supported curves, ROBOT, Heartbleed and more.
- Server certificate validation and revocation checking through OCSP stapling.
- Support for StartTLS handshakes on SMTP, XMPP, LDAP, POP, IMAP, RDP, PostGres and FTP.
- Scan results can be written to a JSON file for further processing.
Let’s get started without wasting time. We know it comes with Kali Linux pre-installed but if not installed in some installation we can install it by using following command:
By applying above command we can install/upgrade SSLyze on our Kali Linux system. Then we can check the help of this tool by using following command:
The screenshot of the command is following:
Now we can read all the options we can use. This is easy to understand we just need to read carefully the help menu and use right flag for what we are trying to get from the server.
In our this article we are going to run a regular scan on a website, by using following command:
Here we have choose a well known website for just an example. We can choose any website or server in the world. We also can put IP address here.
We got the results in the following screenshot:
We can scroll down to see the total result of the scan.
Even not a regular scan we can use many flags to know what we want. We can all the flags (options) on the help menu.
For another example if we need to check for OpenSSL HeartBleed on the server we can use following command:
We know that targeted host Google is not vulnerable to OpenSSL HeartBleed vulnerability. But other domains may be vulnerable.
This is how we can test web server’s using SSLyze on our Kali Linux system. This is very helpful for organizations and testers identify mis-configurations affecting their SSL servers.
Do you enjoy reading our articles? Be sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub for regular updates on new articles. If you want to join our KaliLinuxIn family and be part of a community focused on Linux and Cybersecurity, feel free to join our Telegram Group.
We value building a strong community and are always here to help. Feel free to leave your comments in the comment section, as we read and reply to each one. We appreciate your engagement and look forward to connecting with you.